Microwave Engineering
Uploaded by
Daniel ToddMicrowave Engineering
Uploaded by
Daniel ToddMicrowave Engineering (404183)
Teaching scheme
Examination Scheme
In Semester Assement: Phase I: 30
End Semester Examination: Phase II: 70
Paper: 100 Marks
Lectures/week: 4 Hrs
Text Books
T1. David M. Pozar, Microwave Engineering", Fourth edition, Wiley.
T2. Samuel Y. Liao, Microwave Devices and Circuits, 3rd edition, Pearson
Reference Books
R1. M. Kulkarni, Microwave and Radar engineering, 3rd edition, Umesh Publications
R2. Radar Engineering By G. S. N. Raju
TEACHING METHODOLOGY
Unit 1: Transmission Lines and Waveguides
Topic
8 Hours
References
Introduction to Microwaves engineering: History of Microwaves,
Microwave Frequency bands. Applications of Microwave
General solution for TEM, TE and TM waves
Parallel plate waveguide, rectangular waveguide, coaxial line
Rectangular waveguide cavity resonators, introduction to Circular
waveguide cavity resonators
Stripline, Microstrip line, Parallel Strip line, Coplaner Strip line, Shielded
Strip Line
Unit 2: Microwave Network Analysis
Topic
Impedance and Equivalent voltages and currents
Impedance and Admittance matrices,
R1 (pg 1-10)
T1 (3.1)
T1(3.2,3.3,3.4,3.5)
T1(6.3,6.4)
T1(3.7,3.8), R1(110 TO 11-4)
8 Hours
References
T1 (4.1)
T1 (4.2)
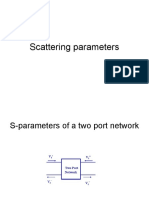
The scattering matrix
T1(4.3)
The Transmission (ABCD) matrix
T1(4.4)
Signal flow graphs,
T1(4.5)
Excitation of Waveguides Electric and Magnetic currents,
T1(4.7)
Excitation of Waveguides Aperture coupling
T1(4.8)
Unit 3: Impedance Matching and Tuning
Topic
Matching with lumped Elements (L networks),
Single stub tuning,
Double stud tuning
6 Hours
References
T1(5.1)
T1(5.2)
T1(5.3)
The quarter wave transformer,
the theory of small reflection,
Binomial matching transformers,
chebyshev multisection matching transformers,
Tapered lines
T1(5.4)
T1(5.5)
T1(5.6)
T1(5.7)
T1(5.8)
Unit 4: Microwave Sources and Solid State Devices
6 Hours
Topic
References
Limitation of conventional tubes
R1(8.2)
Microwave tubes,
R1(8.4)
Velocity modulation,
R2(6.13)
Method of producing the velocity modulation
Principle of operation of two cavity klystron,
R1 (8.5)
reflex klystron principle of operation,
velocity modulation in reflex klystron,
applegate diagram with gap voltage for a reflex klystron.
Principle of operation of Magnetron, hull cutoff condition, advantages of R1(8.8)
slow wave devices,
Principle of operation of TWT.
R1(8.6)
Microwave bipolar transistor, FET,
R1(9.1,9.2,9.3)
Principle of Operation and application of tunnel diode,
R1(9.9)
Principle of operation of Gunn diode, application of gunn diode advantages T2(7-1)
of gunn diode,
principle of operation of PIN diode, applications of PIN diode
R1(9.7)
Unit 5: Microwave Passive and Active Components
Topic
Directional Coupler,
Power Divider,
Magic Tee,
Attenuator
Resonator,
Isolator, Oscillators,
Mixers, with wave guides and
Striplines, Tunable detector
6 Hours
References
T2(4.5)
Unit 6: Microwave Measurements
Topic
Measurement devices:
Slotted line,
Tunable detector,
VSWR meter,
Power Meter,
S-parameter measurement,
6Hours
References
R1(6.3)
R1(6.15)
R1(6.12)
T2(4.6)
R1(7.3.1)
R1(7.3.2)
R1(7.3.3)
R1(7.3.4)
R1(7.3.9)
frequency measurements,
Power measurement,
Attenuation measurement,
Phase shift measurement,
VSWR measurement,
Impedance measurement,
Q of cavity resonator measurement
R1(7.4)
R1(7.5)
R1(7.6)
R1(7.7)
R1(7.8)
R1(7.9)
R1(7.13)
You might also like
- Microstrip Antenna Arrays: Prof. Girish KumarNo ratings yetMicrostrip Antenna Arrays: Prof. Girish Kumar24 pages
- Design and Analysis of Inset Fed Microstrip PatchNo ratings yetDesign and Analysis of Inset Fed Microstrip Patch10 pages
- VIT UNIVERSITY SYLLABUS Ece306 Antennas and Wave Propagation50% (2)VIT UNIVERSITY SYLLABUS Ece306 Antennas and Wave Propagation2 pages
- Microwave Engineering November Am Rr311701No ratings yetMicrowave Engineering November Am Rr3117018 pages
- Radar Engineering and Navigational Aids Question Bank UNIT 3No ratings yetRadar Engineering and Navigational Aids Question Bank UNIT 31 page
- Ec6015 Radar and Navigational Aids - Syllabus-A5No ratings yetEc6015 Radar and Navigational Aids - Syllabus-A52 pages
- 4-SCATTERING MATRIX-15-Jul-2019Material - I - 15-Jul-2019 - 7 - SparametersNo ratings yet4-SCATTERING MATRIX-15-Jul-2019Material - I - 15-Jul-2019 - 7 - Sparameters12 pages
- Antenna Theory by Balanis Solution Manual 3rd Edition PDF100% (1)Antenna Theory by Balanis Solution Manual 3rd Edition PDF331 pages
- Microwave Engineering 3rd Edition 2004 Pozar Solution ManualNo ratings yetMicrowave Engineering 3rd Edition 2004 Pozar Solution Manual288 pages
- Microwave Devices and Circuits (Samuel Liao)No ratings yetMicrowave Devices and Circuits (Samuel Liao)545 pages
- GSN Raju Electromagnetic Field Theory 35 PDF100% (1)GSN Raju Electromagnetic Field Theory 35 PDF4 pages
- Information Theory Coding And Cryptography 3rd Edition Ranjan Bose all chapter instant download100% (1)Information Theory Coding And Cryptography 3rd Edition Ranjan Bose all chapter instant download55 pages
- Antenna and Wave Propagation: EngineeringNo ratings yetAntenna and Wave Propagation: Engineering1 page
- Microwave Engineering & RF MEMS: Detailed Course OutlineNo ratings yetMicrowave Engineering & RF MEMS: Detailed Course Outline18 pages
- IAT-III Question Paper With Solution of 18EC63 Microwave and Antennas July-2023-Sutapa SarkarNo ratings yetIAT-III Question Paper With Solution of 18EC63 Microwave and Antennas July-2023-Sutapa Sarkar17 pages
- 6) Noise Characterization of A Microwave ReceiverNo ratings yet6) Noise Characterization of A Microwave Receiver17 pages
- Introduction To Microwave Circuits & Systems100% (1)Introduction To Microwave Circuits & Systems15 pages
- Angle Modulation: Angle Modulation Is Defined As A Process in Which The AngleNo ratings yetAngle Modulation: Angle Modulation Is Defined As A Process in Which The Angle10 pages
- MATLAB Programming Tutorial - Version 05-: Electromagnetic Fields Theory (BEE3113)100% (1)MATLAB Programming Tutorial - Version 05-: Electromagnetic Fields Theory (BEE3113)32 pages
- Periodic Structures Image Parameter Method Insertion Loss Method Filter TransformationNo ratings yetPeriodic Structures Image Parameter Method Insertion Loss Method Filter Transformation63 pages
- Chapter 13 Inspection Policies and Housing Quality StandardsNo ratings yetChapter 13 Inspection Policies and Housing Quality Standards21 pages
- DVD Home Theater System: Owner'S ManualNo ratings yetDVD Home Theater System: Owner'S Manual44 pages
- 2021-Briefing Note-Uganda UNSDCF 2021-2025-EN-2021.01.18No ratings yet2021-Briefing Note-Uganda UNSDCF 2021-2025-EN-2021.01.1811 pages
- Work Flow Creation Steps For Parked DocumentNo ratings yetWork Flow Creation Steps For Parked Document22 pages
- (Full Topic) Ielts Speaking 9-12 - Ielts Quoc SonNo ratings yet(Full Topic) Ielts Speaking 9-12 - Ielts Quoc Son21 pages
- Crime and Punishment - Teacher's VersionNo ratings yetCrime and Punishment - Teacher's Version8 pages
- Which Company Did You Visit?: We Visited Himjal Beverages Privated Limited (Kinley)No ratings yetWhich Company Did You Visit?: We Visited Himjal Beverages Privated Limited (Kinley)3 pages
- TAFJ-Eclipse Debugging T24 JBC Invoked Via IRIS100% (1)TAFJ-Eclipse Debugging T24 JBC Invoked Via IRIS8 pages
- 06-fc595cl Turbocharger Number 1 Speed High - Data Valid But Above Normal Operational Range - ModeratelySevere Level PDFNo ratings yet06-fc595cl Turbocharger Number 1 Speed High - Data Valid But Above Normal Operational Range - ModeratelySevere Level PDF3 pages
- Gayatri Satish Mane: SES Polytechnic (Solapur)No ratings yetGayatri Satish Mane: SES Polytechnic (Solapur)2 pages
- 8 Probabilistic Ground Motions in Earthquake Resistant Design of BuildingsNo ratings yet8 Probabilistic Ground Motions in Earthquake Resistant Design of Buildings34 pages
- Economic Plantwide Control Design Procedure and Case StudiesNo ratings yetEconomic Plantwide Control Design Procedure and Case Studies68 pages
- The Role of Customer Engagement Behavior in Value Co-Creation: A Service System PerspectiveNo ratings yetThe Role of Customer Engagement Behavior in Value Co-Creation: A Service System Perspective15 pages