Bacterial Indentification (Micro)
Uploaded by
Aryaman MohapatraBacterial Indentification (Micro)
Uploaded by
Aryaman MohapatraCITRATE UTILISATION TEST
Done for the ability of an organism to utilise citrate as the sole source of carbon &energy
source for growth and ammonium salt as the sole source of nitrogen.
Medium Constituents :
1)Simmons citrate: NaCI-5gm
Indicator:- bromothymol blue MgSO4-0.2gm
Green Blue NH4H2PO4-1gm
pH 6.8. pH 7.6 KH2PO4-1gm
NaC6H507.2H20-5gm
2) koser's medium Distilled water-1 Liter
Indicator:- no indicator
Noturbidity --turbidity
Simmons's citrate medium= Koser's medium +agar 20 gm + Bromothymol blue 0.2%(40 mil)
Principle:
Na citrate NH4dihydrogen phosphate
(sole source of carbon ) (Sole source of N2)
Citrate permease enzyme) Breaks down to release
NH3(ammonia)
Transport citrate into the bacterial Alkaline pH
cell
TCA cycle
Citratase
Citrate Oxaloacetate + acetate
Pyruvicacid+ CO2
Binds to Na + H20 NaHCO3
(Alkaline pH)
Result:
Positive control
Enterobacter aerogens
Bromothymol blue Bromothymol blue Negative control
pH 6.8 pH 7.6 Escherichia coli
GREEN BLUE
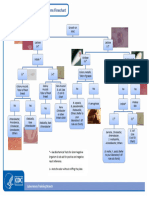
TRIPLE SUGARIRON (TSI)
Composition
1)Three sugar( glucose, lactose, sucrose)
(1:10:10)
2)Sodium thiosulphate:- provide sulphur to bacteria.
Combines with H+ ion in acidic pH to form H2S.
3) Ferrous sulphate:- provide Fe+3 which further combines with H2S to form
ferrous sulphide(black precipitates)
4) Phenol red:- pH indicator( <6.8=yellowand >7.4=red)
5) Peptone:-under goes oxidative deamination to produce alkalinity.
Principle:
Fermentation of glucose( 1st 8 hr)-acid production
Oxidative deamination of peptone( 8-16hr)-NH3 production(alkaline)
Sucrose/lactose fermentation or sucrose + lactose fermentation
(Increase acid production, overcome the alkalinity of deamination of peptone)
Outcome :
Acid production Gas production H2S production
AA K/A K/K Present Absent Yes No
E. coli SalmonellaPseudomonas E. coli Pseudomonas S.parathyphi-B| S.parathyphi A
S. typhi Shigella
Klebsiella Shigella Acinetobactor Klebsiella 'Acinetobactor Proteus
(LF) (NLF) (NLF)
Control Red Slant Red Slant Yellow Slant Yellow Slant Red Slant
Red Butt Yellow Butt Yellow Butt Yellow Butt Yellow Butt
No Gas No Gas, +Gas + Gas + (Gas
B8èT
TeT
PHENYLALANINE DEAMINASE TEST
PRINCIPLE:
Phenylalanine is an amino acid that on deamination forms a ketoacid
i.e. phenylpyruvic acid.
Proteus, Morganella & Providencia possess the deaminase enzyme
required for the conversion.
PPAtest depends on the detection of phenylpyruvic acid in the test
medium after growth of the test organism.
Ifa visible green colour develops on addition of 10% ferric
chloride(FeCI3), then test is positive.
Phenylalanine
Phenylalanine Phenyl pyruvic acid + NH3
deaminase
Acid
Phenylpyruvic acid + Fe3 Green colour complex
act (pH=7.3)
MEDIA:- Source of phenyl alanine-yeast extract
PROCEDURE:
Agar slantof the medium is inoculated with single colony
of test organism isolated in pure culture
Incubate at 37 degree
For 18-24 hr
4-5drops of FeCI3 is added directly to the surface of agar
INTERPRETATION:
Immediate appearance of intense green colour indicate
presence of fnylpyruvic acid i.e. positive test
Positive control:
Proteus species
Negative control:
E. coli
Positive Negative
Pnenyle Alanine Deaminase (PPA) Test
Bacteria possessing the enzyme pnenyle alanine
deaminase will
convert the phenyle alanine in the medium to phenyl pyruvic acid.
Principle : The test bacteria after inoculation into the test medium and
incubation if produces pyruvic acid - then agreen colour develops
upon
addition of a solution of 10% ferric chloride.
Media & Reagents - Phenyl alanine agar,ferric
chloride,distilled
water PH-Z.3
Interpretation : Immediate appearance of intense green colour indicates - +ve
+ve Control : Proteus, Providencia, Morganella.
-ve Control Esch coli, Klebsiella.
eosoa
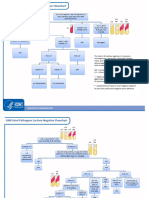
Urea Hydrolysis Test
Urease producing bacteria can split urea present in the medium to
produce ammonia that makes the medium alkaline.
Media- Christensen's urea agar, Stuart's urea broth.
Christensen's urea medium
Peptone 1g control + ve + Ve Ve
Glucose 1g
Sodium chloride 5g
Monopotassium phosphate 28
Urea 20g
Phenol red (indicator) 0.012g
Arar 15g
Distilled water 1L
Final pH 6.8
urease
NH2-C0-NH2 + Hz0 2NH3 + 2 CO2
Phenol red indicator changes to pink color in alkaline medium.
Incubation- 35° C for 18-24 hours.
Urease test positive for : Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus species,
Helicobacter pylori.
Urease test negative for :E.coli, Shigella, Salmonella.
Quality control
Positive control : Proteus species
Positive control (weak) : Klebsiella species.
Negative control : E.coli
Rm
Supertek
1550
Aimof the test; Sugar fermentation test
To assess the ability of bacteria to ferment a specific carbohydrate
To differentiate bacteria based on their carbohydrate fermentation pattern
Principle;
" Different bacteria have different abilities to ferment specific carbohydrate
While fermenting carbohydrates, organic acid are producedas end products, this causes
decrease in pH of the medium which can be detected by pH indicator.
If the bacteria releases gas during carbohydrate fermentation, it is trapped as an air
bubble in inverted Durham's tube.
Constituents:
1) nutrient media as base:-peptone water/serum agar/serum peptone water
2)carbohydrate:-glucose, lactose, manitol, maltose, galactose, arabinose, xylose etc.
3)reagent: Table 1. pH Indlcators for Cartbowdrate Fermentation Media
Ado
Andrade's indicator( acid fuschin+NaOH) pH Indicator
Uninoculated Media (fermentation Alkaline (negative)
phenol red pH Colo ph Color pH Color
7.1 12.0 Yellow,
Bromocresol purple Andrade's
Bromcresol purple
7.2
7.4
Light pink
Deep purple
5.0
5.2
P1nk-red
Yellow
14.0
6.8
colorless
(BCP) Purple
Bromothymol blue Bromthymol blue
(BTB)
7.0 Green 6.0 Yellow 7.6
Deep Prussian
blue
Reddish
Procedure : Phenol red 7.4
orange
6.8 Yellow 8.4 Pink-red
Fresh culture of sample bacteria inoculated in broth
Incubate at 37 degree/18-24hr
Result: Observe colour change and gas formation
Gas
Bacteria Ferment
production
E. coli
Glucose, sucrose, Yes
Sugar fermentation test
manitol, lactose
k. pneumonia
Glucose,sucrose, Yes
manitol, lactose
Pseudomonas Glucose No
Glucose, manitol,
Salmonela typhi maltose
No
P. mirabilis Glucose Yes
uinoculated Not fernented fermented with Annly fermented with A&G
Applications
Presumptive identification of bacteria
cOBMIVCo
INDOLE TEST
PRINCIPLE:
Indole isametabolic degradation product of amino acid tryptophan.
amino acid
Bacteria those posses the enzyme tryptophanase can cleave the
tryptophan to product Indole.
Tryptophanase Indole + pyruvic acid+ NH3
Tryptophan
Kovac's reagent
Indole Redcolour complex
(di-(4-(indole-3-yl-methylene) -2,5
cyclohexadien-1-ylidene]-di-methyl
ammonium salt)
Kovac's reagent:-para-di-methyl-amino-benzaldehyde
PROCEDURE:
The test bacteria is inoculated in peptone water
and
incubated overnight at 37 degree C 252908.1608
Kovacs Reaent for cdnlcal
dagnosb
100 m
Add 10-15 drops of kovac's reagent
RESULT:
Development of light fuchsia red colour at the interface of the reagents-brott
within a seconds indicates positive test.
Indole positive Indole negative
Positive control:
Escherichia. coli
Negative control:
Klebsiella pneumoniae
B
INDOLE TEST
Indole is a metabolic degradation product of aminoacid tryptophan.
Bacteria those posses the enzyme tryptophanase can cleave the aminoacid
tryptophan to produce Indole.
Principle of Detection
Indole forms a redcolour complex when reacts with Kovac's
reagent i.e.
Paradimethyle aminobenzaldehyde.
Test bacteria is inoculated in peptone water & incubated
overnight at 37'C,
than 10drops of Kovac's reagent is added.
Interpretation : Development of a light fuschia red colour at the interface of the
reagents broth within seconds indicates -Positive Test.
.Positive Control -Esch .coli, Negative Control Klebsiella
pneumoniae.
I120AO
INDOLE TEST
sid ryptopi
degradationproduct o amino acid
cleavethe
tophanasecan
INDOLE TEST
tryplupian.
o10 acid acid
ation product yethe
amino
You might also like
- PHM321Y Antibiotics: Amoxicillin Amoxicillin-ClavulanateNo ratings yetPHM321Y Antibiotics: Amoxicillin Amoxicillin-Clavulanate3 pages
- Biochemical Tests: I. Carbohydrate FermentationNo ratings yetBiochemical Tests: I. Carbohydrate Fermentation5 pages
- Biochemical Tests Enterobacteria IdentificationNo ratings yetBiochemical Tests Enterobacteria Identification10 pages
- Biochemical Tests For Bacterial Identification Biochemical Tests Triple Sugar Iron Agar (Tsi)No ratings yetBiochemical Tests For Bacterial Identification Biochemical Tests Triple Sugar Iron Agar (Tsi)5 pages
- Biochemical Testing: EnterobacteriaceaeNo ratings yetBiochemical Testing: Enterobacteriaceae14 pages
- MLS 441 Biochemical Reactions 4th LectureNo ratings yetMLS 441 Biochemical Reactions 4th Lecture39 pages
- Biochemical Identification of Gram (-) Bacteria: I. Carbohydrate UtilizationNo ratings yetBiochemical Identification of Gram (-) Bacteria: I. Carbohydrate Utilization4 pages
- Biochemical evaluation of microorganismsNo ratings yetBiochemical evaluation of microorganisms27 pages
- Media & Biochemical Tests: Laboratory ObjectivesNo ratings yetMedia & Biochemical Tests: Laboratory Objectives36 pages
- Test Media Purpose Components Reagents Expected Result Quality Control Gram StainNo ratings yetTest Media Purpose Components Reagents Expected Result Quality Control Gram Stain7 pages
- Diagnostic Microbiology: Biochemical Tests, Immunoassays and Molecular DiagnosticsNo ratings yetDiagnostic Microbiology: Biochemical Tests, Immunoassays and Molecular Diagnostics62 pages
- Biochemical Identification of Gram-Negative Bacteria(1)No ratings yetBiochemical Identification of Gram-Negative Bacteria(1)32 pages
- Water Analysis: - Detect The Presence of Coliform BacteriaNo ratings yetWater Analysis: - Detect The Presence of Coliform Bacteria35 pages
- Biochemical Test Bacteriology Laboratory 2024No ratings yetBiochemical Test Bacteriology Laboratory 202449 pages
- Components Positive Result Negative Result PrincipleNo ratings yetComponents Positive Result Negative Result Principle2 pages
- Isolation and Identification of Enteric OrganismsNo ratings yetIsolation and Identification of Enteric Organisms7 pages
- 10.biochemical Tests For Identification of BacteriaNo ratings yet10.biochemical Tests For Identification of Bacteria20 pages
- Biochemical Reactions For Identification of BacteriaNo ratings yetBiochemical Reactions For Identification of Bacteria9 pages
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and Manures5/5 (1)
- BIOL 2420: Microbiology For The Health Sciences Biochemical Test ChartNo ratings yetBIOL 2420: Microbiology For The Health Sciences Biochemical Test Chart2 pages
- Gram Negative Rods NonStool Pathogens FlowchartNo ratings yetGram Negative Rods NonStool Pathogens Flowchart1 page
- Indole Test: General Procedure For Performing Imvic Tests and Their InterpretationsNo ratings yetIndole Test: General Procedure For Performing Imvic Tests and Their Interpretations2 pages
- SOP of Reference Cultures Maintenance and Usage - Pharmaceutical GuidanceNo ratings yetSOP of Reference Cultures Maintenance and Usage - Pharmaceutical Guidance9 pages
- GNR Stool Pathogens Lactose Negative FlowchartNo ratings yetGNR Stool Pathogens Lactose Negative Flowchart2 pages
- IMViC Test - Principle, Result Chart, Examples, UsesNo ratings yetIMViC Test - Principle, Result Chart, Examples, Uses20 pages
- Diversity of Biofilm-Forming Bacteria in Chinnamuttom Harbor of Southeast IndiaNo ratings yetDiversity of Biofilm-Forming Bacteria in Chinnamuttom Harbor of Southeast India7 pages
- Methyl Red and Voges-Proskauer Test ProtocolsNo ratings yetMethyl Red and Voges-Proskauer Test Protocols9 pages
- Result Form - Enterobacteriales - De Castro - CopyNo ratings yetResult Form - Enterobacteriales - De Castro - Copy3 pages
- Johnson Et Al 1966 Biochemical Differentiation of the Enterobacteriaceae With the Aid of Lysine Iron AgarNo ratings yetJohnson Et Al 1966 Biochemical Differentiation of the Enterobacteriaceae With the Aid of Lysine Iron Agar6 pages